| PELAGIC COMMUNITIES |
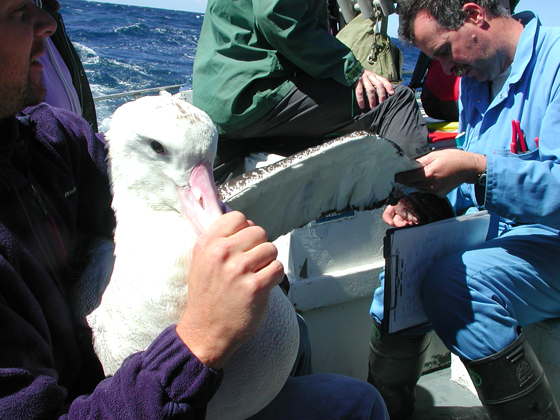
Masters of the storm - Foraging for months across the ocean in conditions of strong wings and high waves, seeking no shelter during storms, enduring tropical heat and polar sleet, soaring continuously through air with a gliding efficiency exceeding that of the most perfectly built human sailplane ¢ the albatrosses (genus Diomedea) are true masters of the sky. Named after Diomed after Trojan Wars, this magnificient bird has a wingplan of nearly 3.6 meters. |
|
Baby albatros |
Phytoplancton: Dinoflagellates -http://www.geo.ucalgary.ca/~macrae/palynology/dinoflagellates/dinoflagellates.html |
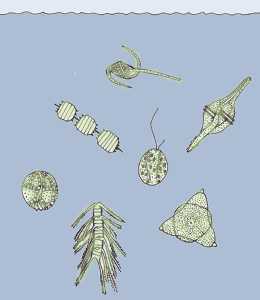
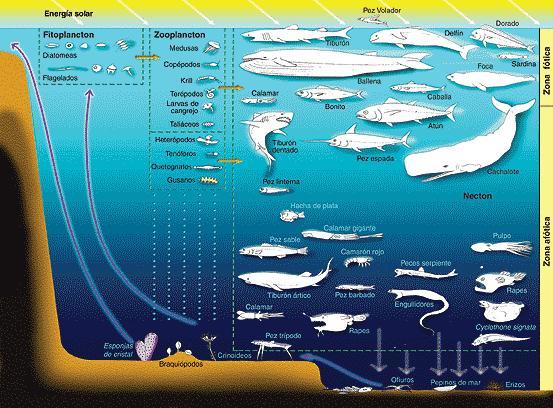
Phytoplankton |
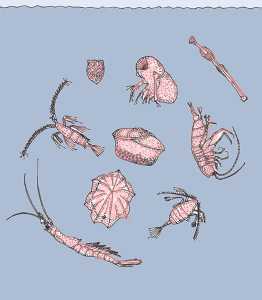
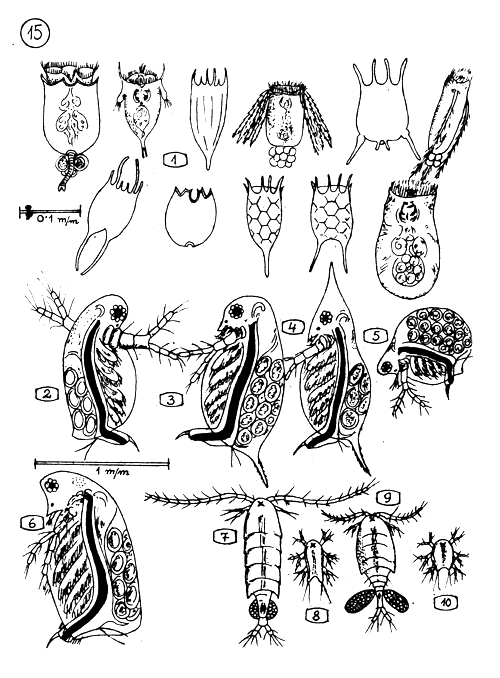
Zooplankton |
|
Zooplankton |
|
|
necton (fish and mammals) |
|
|
Necton: Cephalopod |
|
Nautilus |
The Legend of Architeuthis that cat weight 150 kg |
the Giant Squid Architeuthis |
Carcharodon - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Megalodon |
Whale Shark (Rhineodon typus) |
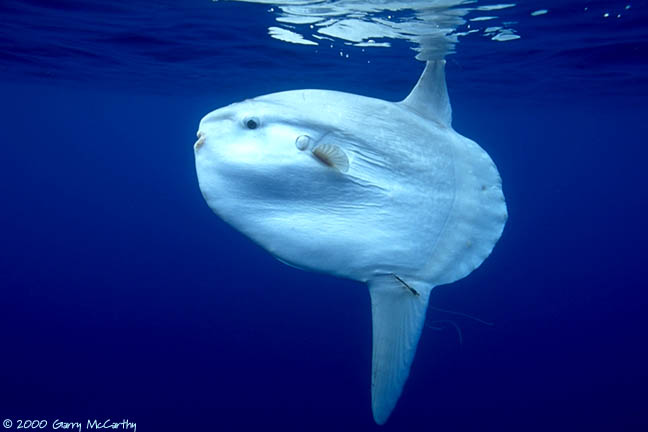
Sunfish |
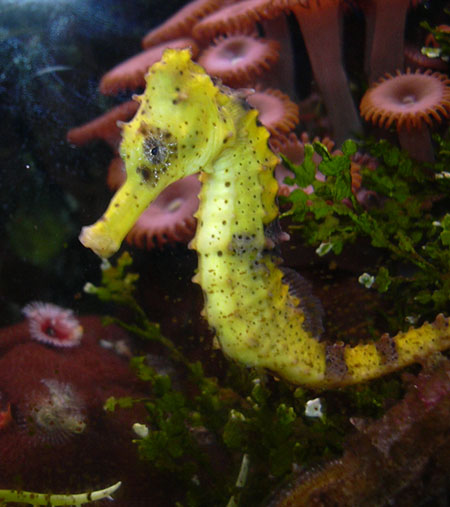
Seahorse |
|
Bony Fish Fossil |
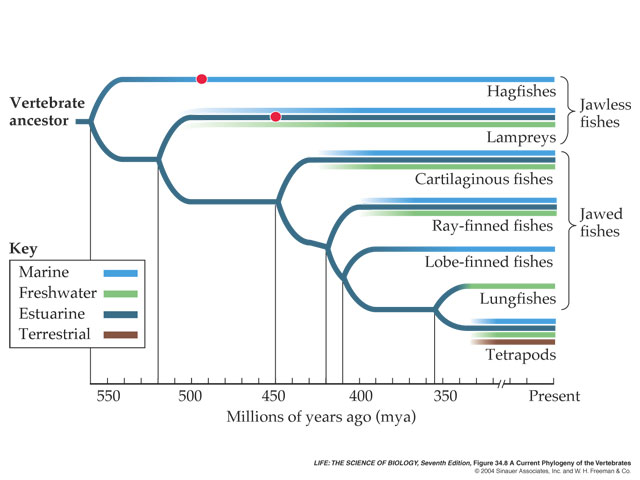
Phylogenetic Relationships Among Living Vertebrates |
Evolution of the bony fishes (actinopterygians and sarcopteryigians) depicted the old-fashioned, "branching tree" way. The relationships among the various lobe-finned fishes (crossopterygians, lungfish, coelacanths) and the amphibia differ from those shown in Figure 1, which is based principally on molecular evidence. From Romer, A. S. 1964. The Vertebrate Body. W. B. Saunders. Philadelphia |
|
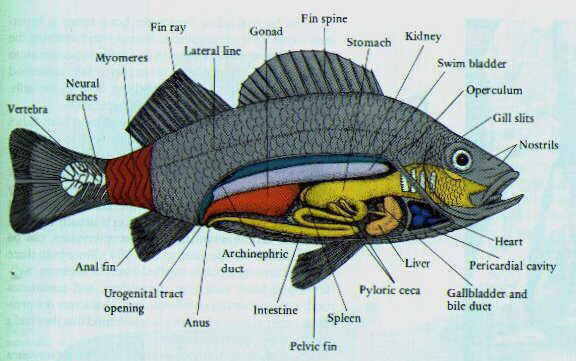
Fish are cold-blooded animals that live in water. They have a streamlined body design and are covered with scales that reduce friction. Most are excellent swimmers. There are over 27,000 species, making them the most diverse vertebrates on Earth. This poster shows the three major clades. The jawless fish, the cartilaginous fish, and the bony fish. The latter dominates the poster, as all the orders / clades are explored. |
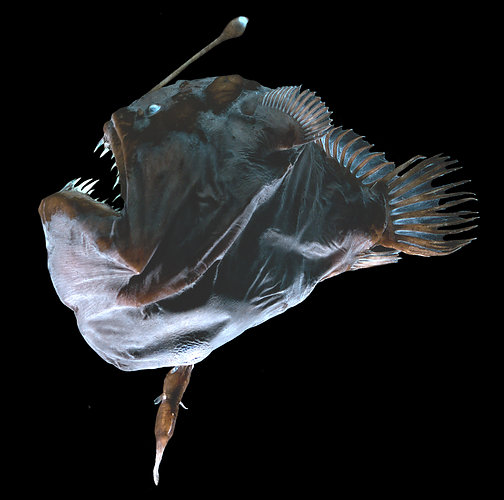
Melanocetidae carries a permanently attached male. |
NECTON
Most nekton animals are vertebrates (animals with backbones), but a few representatives are invertebrates (squids and nautiluses and some species of shrimplike arthropods).
Important nektonic animals include cephalopods, shrimps, fishes, seabirds, and marine animals. Each has a continuously evolving suite of adaptations that allows it to meet the challenges of the marine environment.
Squids and Nautiluses
The mollusks (with clams and snails) are the cephalopods (squids, nautiluses and octopuses).
Shrimps and Their Relatives
Arthropoda includes the copepods, krill, lobsters, shrimps, crabs, and barnacles and is the most successful animal group in the Earth. Their most important innovation is an exoskeleton. The larger species are often called prawns.
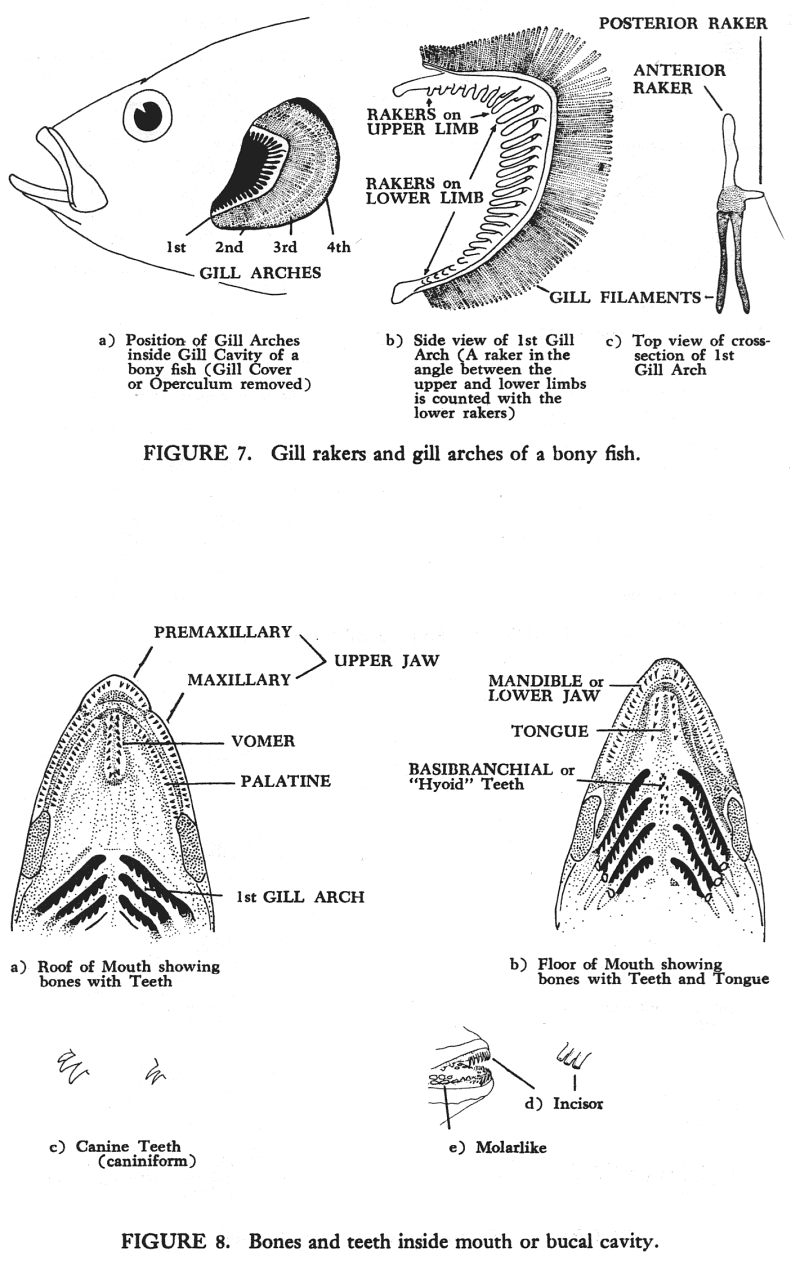
Fishes
The Cartilaginous Fishes
Chongrichthyes (sharks, skates, rays, and chimaeras) ¢ skeleton from cartilage
The Bony Fishes
Osteichthyes
Teleostei
The Problems of Fishes
Movement, Shape, and Propulsion
Maintenance of Level
Swim bladders
Gas Exchange
Gill mambranes
Feeding and defense
Schooling behavior
There are more species of fishes, and more individuals, that species and individuals of all other vertebrates combined. Fishes are divided into two major groups based on the material forming their skeleton.