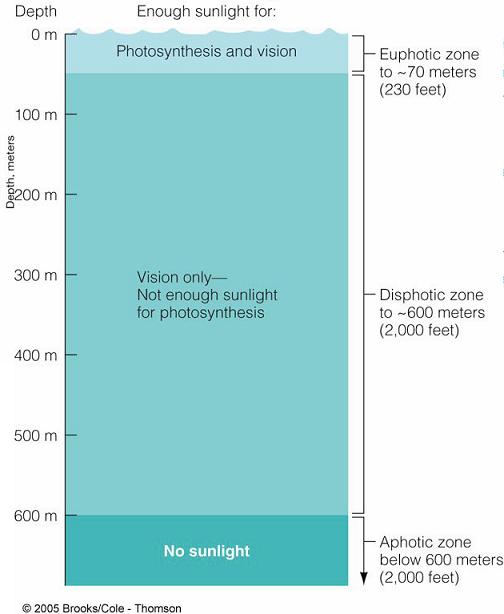
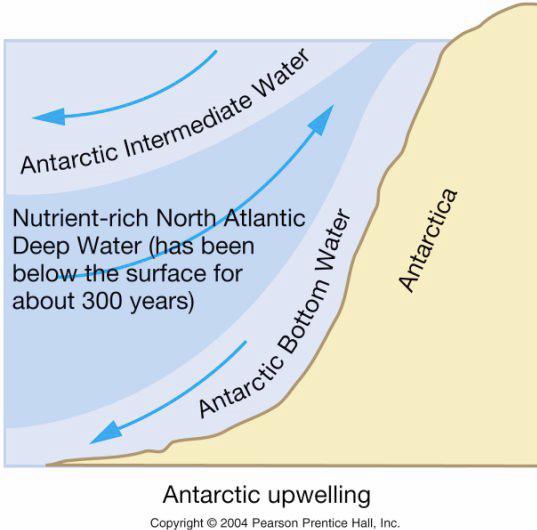
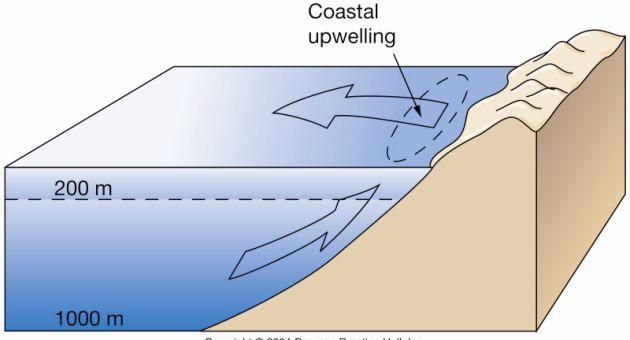
| Earth System History |
|
|
|
|
|
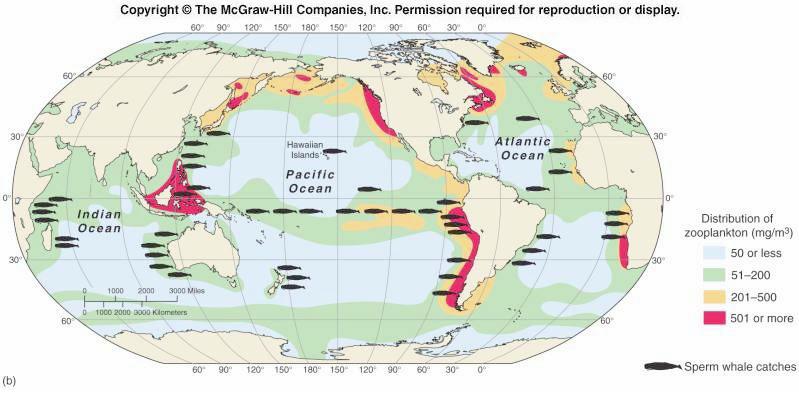
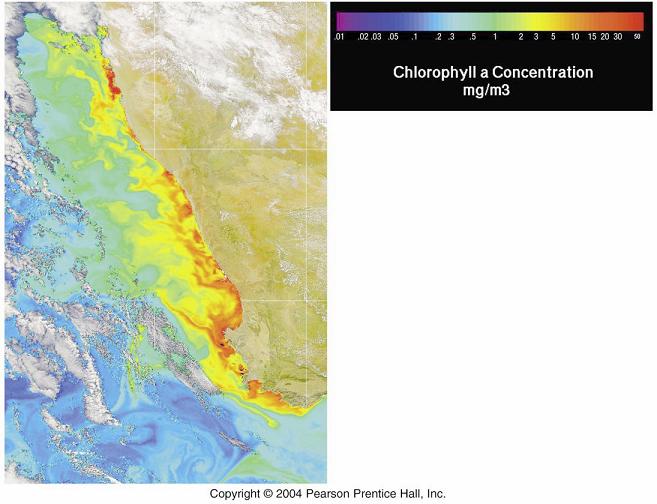
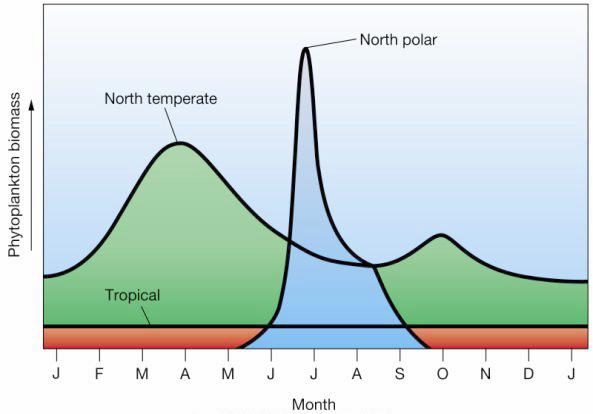
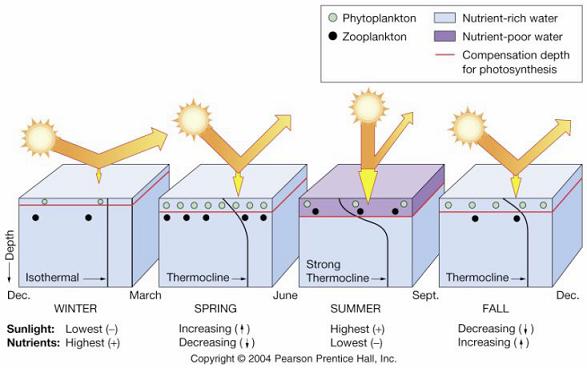
This figure shows us thatproductivity is very low in the tropical oceans all yearlong. How can this be? There is abundant sunlight in the tropics! But in fact, thatÆs the problem. |
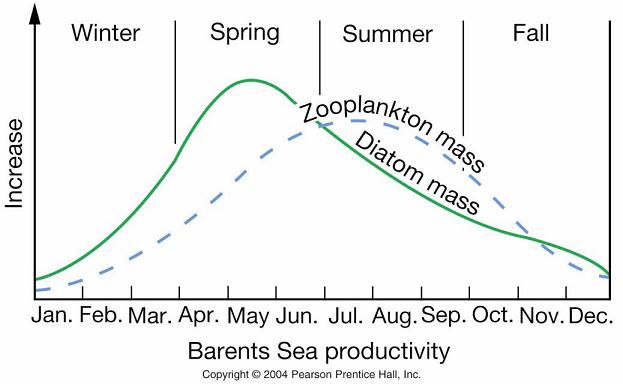
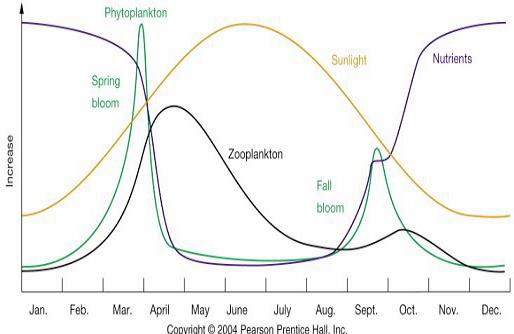
Why is there ōlag timeö between the increase in diatoms and the increase in zooplankton? |
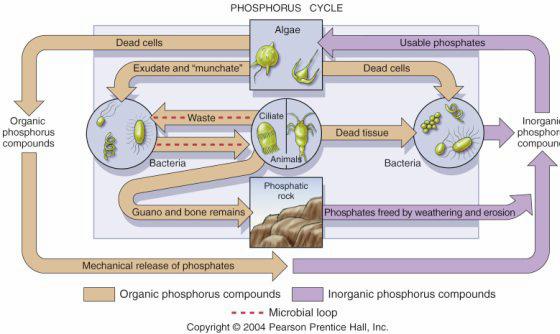
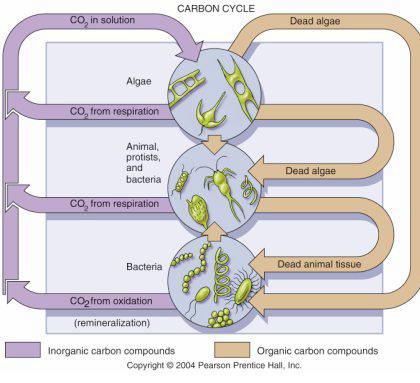
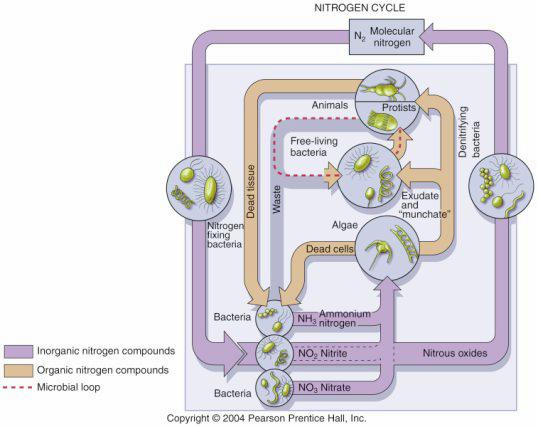
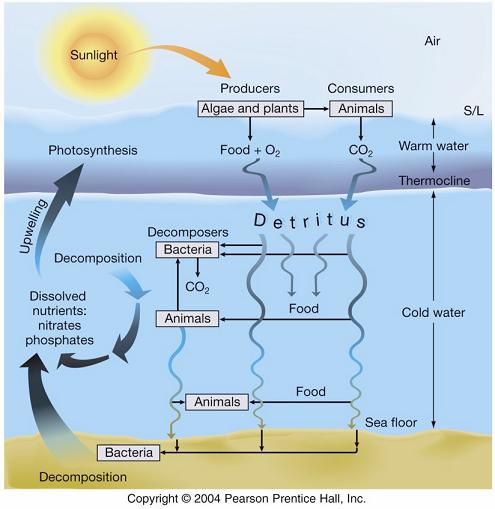
Biogeochemical cycles(including C, P, N) |
Biogeochemical cycles(including C, P, N) |
Biogeochemical cycles(including C, P, N) |
|
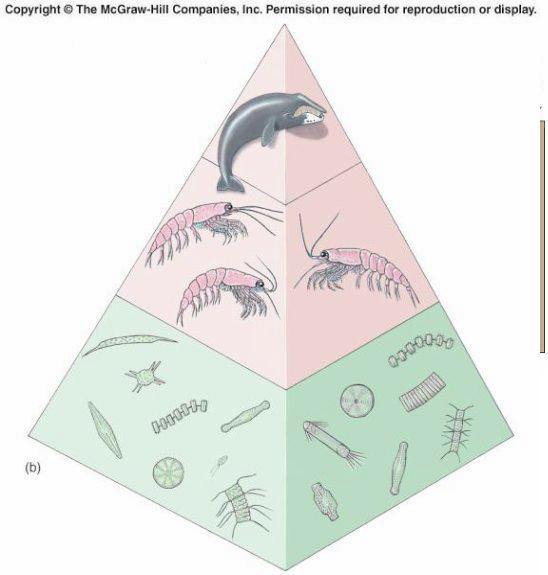
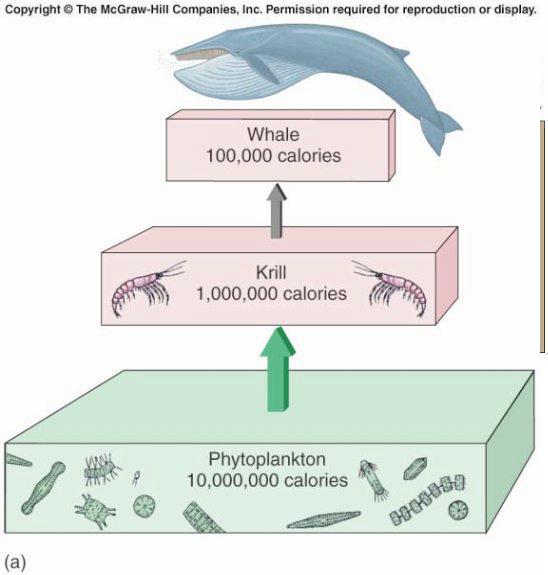
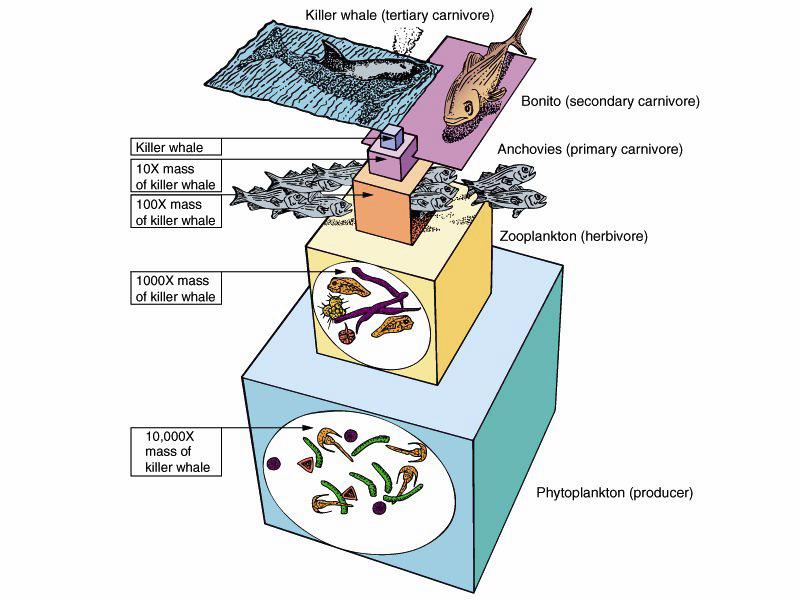
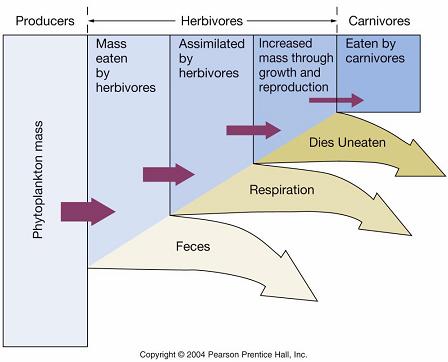
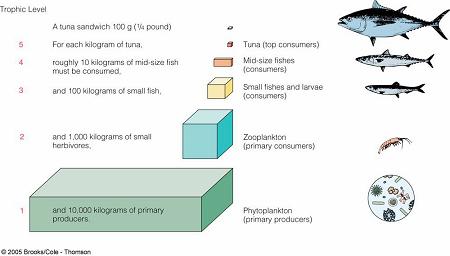
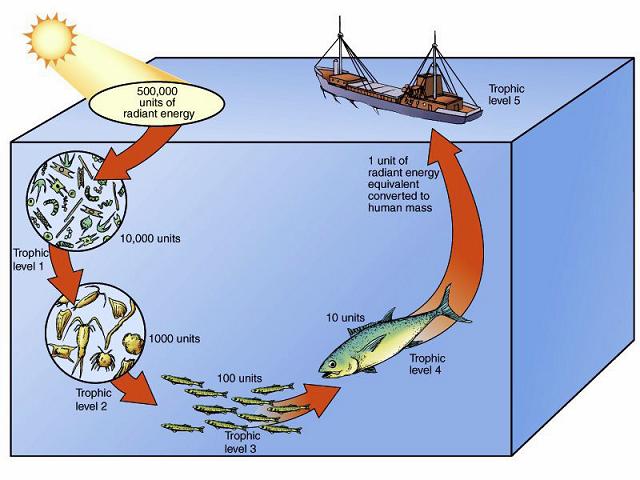
Trophic Pyramid |
|
|
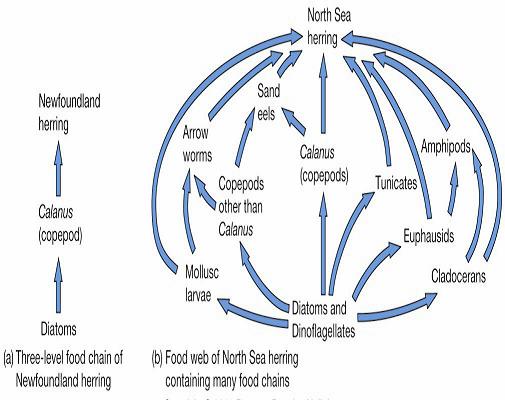
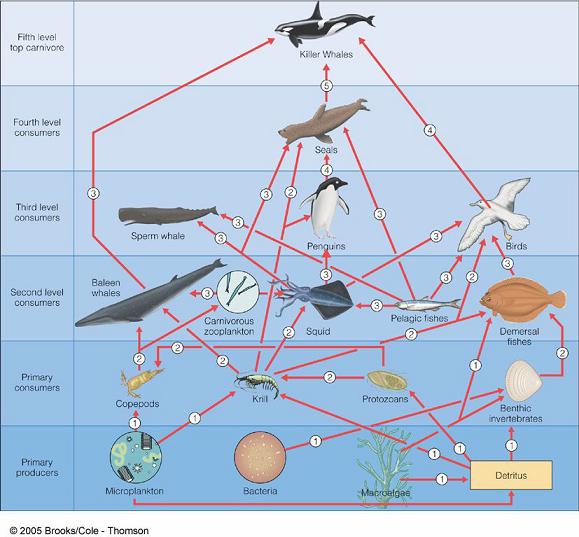
Food Chains vs. Food Webs |
|
|
|
|
Seasonal Productivity in Temperate oceans,Northern Hemosphere |
Seasonal Productivity in Temperate oceans,Northern Hemosphere |
|
|
|
|
Trophic Level |
|
|
|
Seasonal
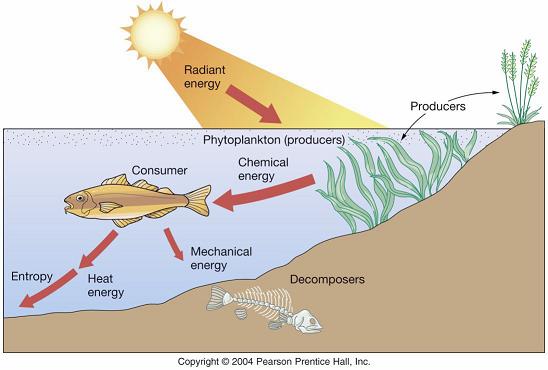
Energy & Food
Photosynthesis
& Respiration
Chemosynthesis
Classification & Systems of Liiviing Thiings
Ģ Hierarchy: Biosphere to Atom
Ģ Taxonomy (classification & naming)
¢ Artificial, Linnaean, Natural; The ō6 Kingdomsö
Ģ Phylogeny (evolutionary relationships)
Ģ Species Diversity
¢ Abundances; Some mechanisms for speciation
Ģ Ecosystems (= community + habitat)
Ģ Communities (of different species)
¢ Change; Interactions (+, ¢, o)
Ģ Populations (of one species)
¢ Distribution patterns; Growth & change; Limiting factors
Ģ Mass extinctions
The Sun heats the ocean surface, creating a strong
thermocline, with warm water on top of cold water. The cold
water down below contains many nutrients, but these cannot
get up to the surface because of the thermocline. Thus,
tropical oceans tend to have low primary productivity
Ecology = The study of distribution and abundance of
species and their relationship to the environment. (The
study of ecosystems.)