| Making Maps |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data Types, Legends, and Classification Types
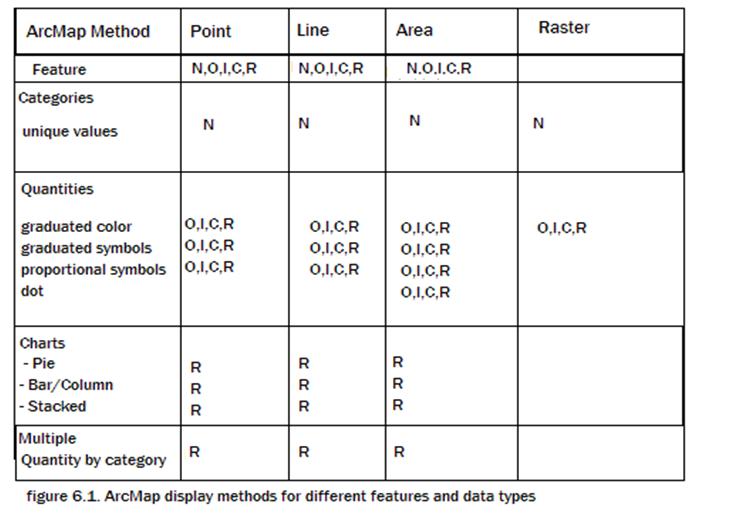
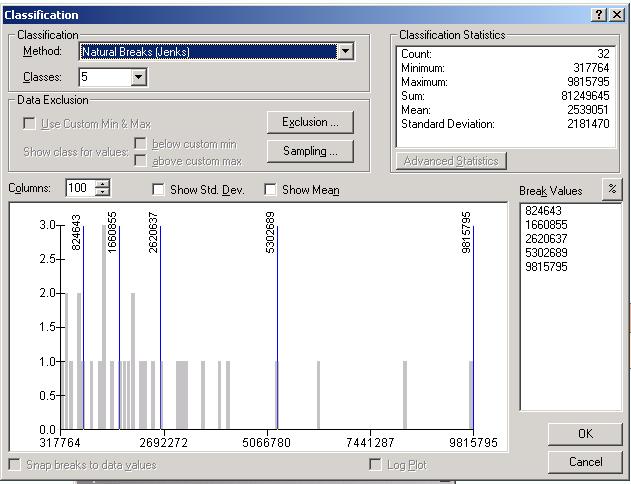
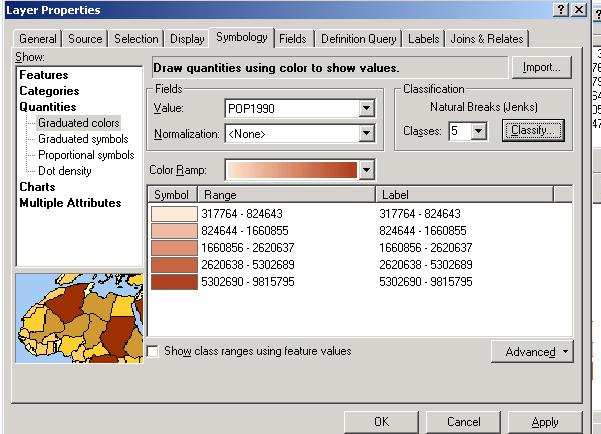
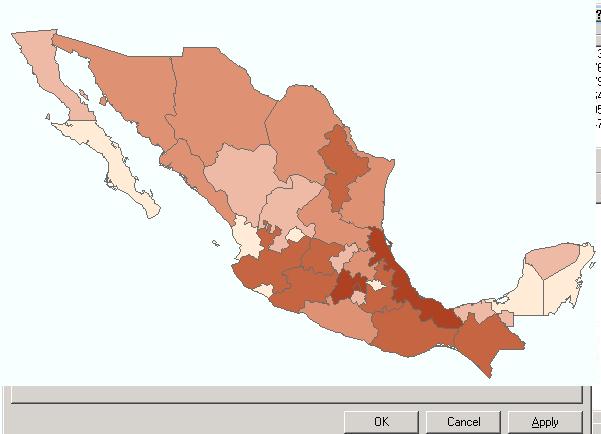
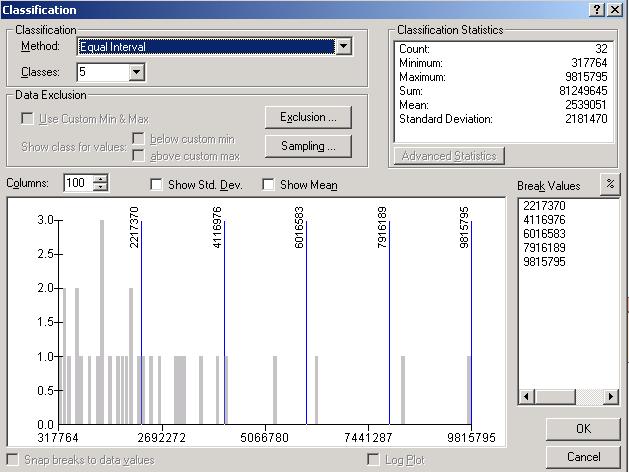
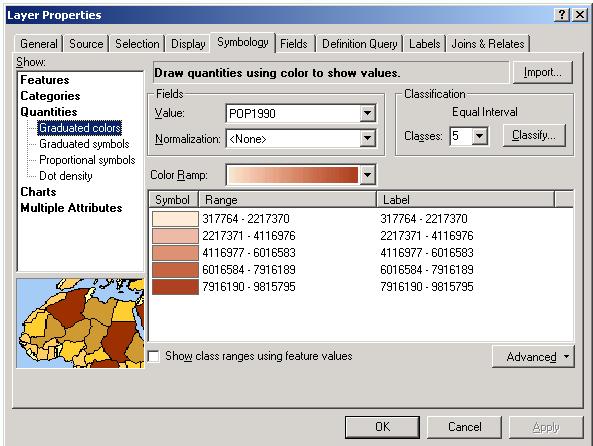
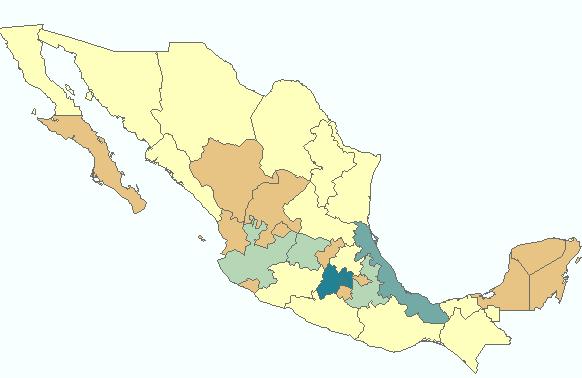
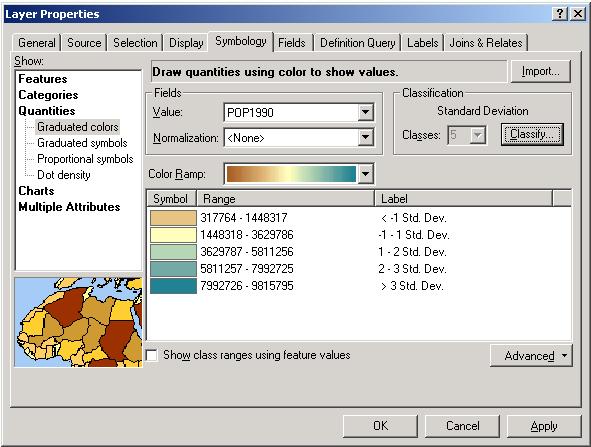
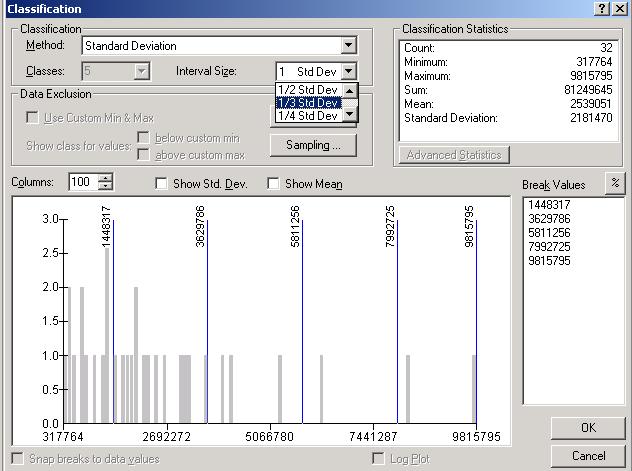
Thematic Mapping with ArcMap
A wide wariety of thematic map types have been developed to portray attributes of geographic features.Attribute data types include qualitative (nominal) or quantitative (ordinal, interval, cyclic, or ratio).
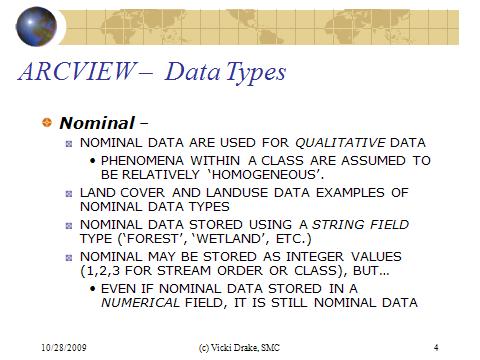
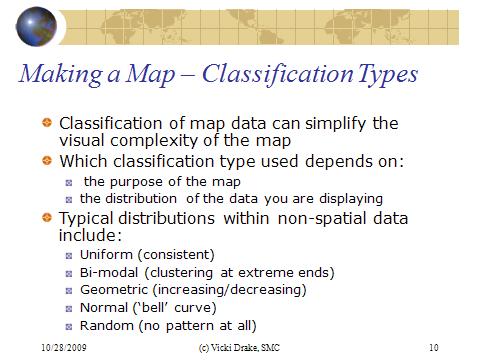
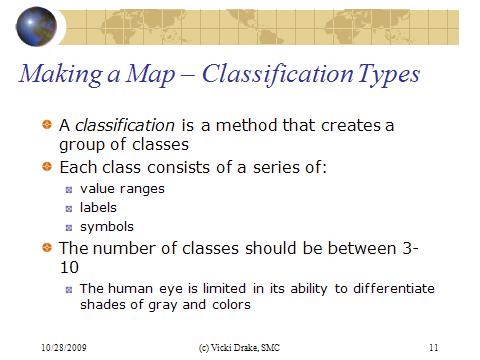
Nominal - the nominal data type is used for qualitative data, associated with categorical or class data. Phenomena within a class are assumed to be relative homogeneous. Land cover and land use data are typical examples of nominal data. Nominal data are stored using a string-type field (as opposed to a numeretical-type field)
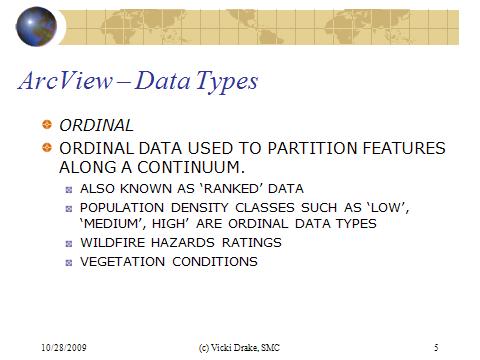
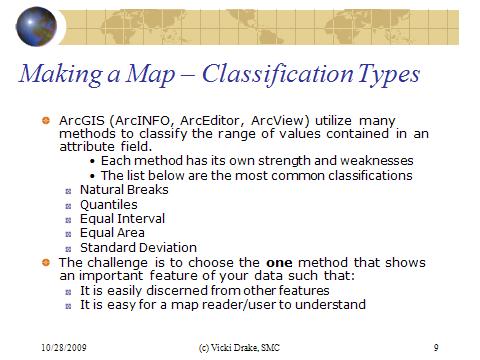
Ordinal data type is used to partition features along a continuum. It is also referred to a rank data. Population density classes, wildfire hazard ratings, vegetation conditions ...
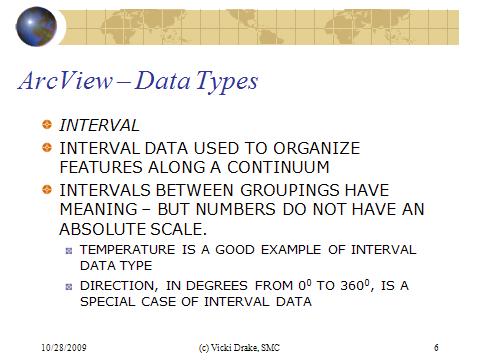
The interval data type is also used to organize features along a continuum and the intervals between the groups have meaning - but the numbers do not have an absolute scale. Temperature is a good example of this type, because "0" value for temperature is atributary - that is, you couldn''t state that 60F is twice as hot as 30F.
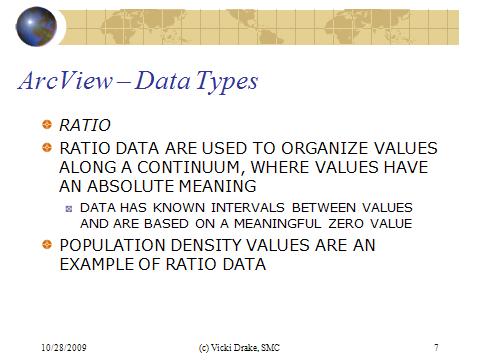
The ratio data is used to organize values along a continuum where the values do have an absolute meaning. The numbers of acres of a particular crop in a fermer''s field, the number of people per county or square mile... With ratio data, computations are possible, as well as statistical summaries.
The Cyclic data type is used to characterize directional attributes, such as aspect on a mountain slope, or degrees on a compass. This data type is a special data type from ratio data, because you cannot always average values, such as compass degrees. The average between 80 and 100 degrees is 90, but between 350 and 10 - 0, not 180.
ArcMap offers a variety of map types to display qualitative or quantitative data.
next
GIS and Cartography
Map types and GIS
Working with Layers