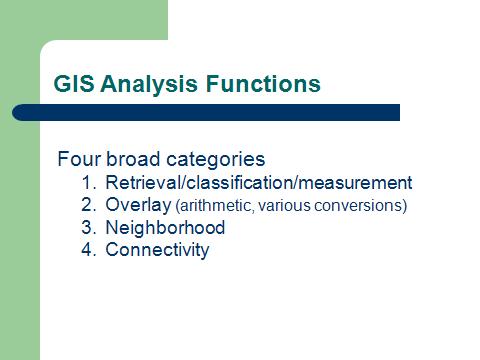
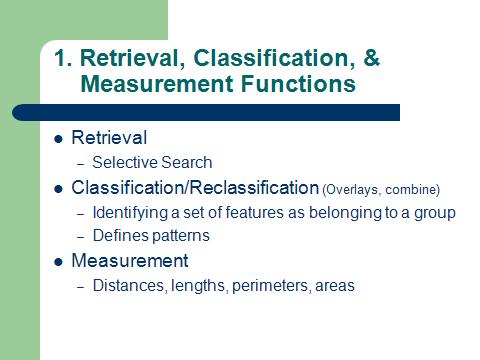
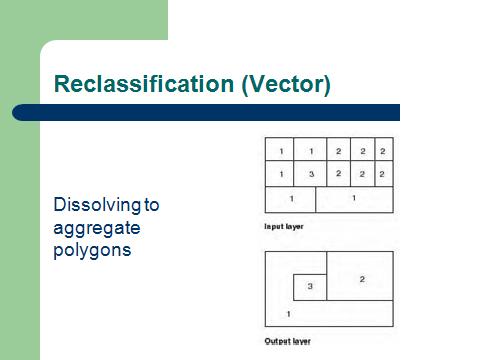
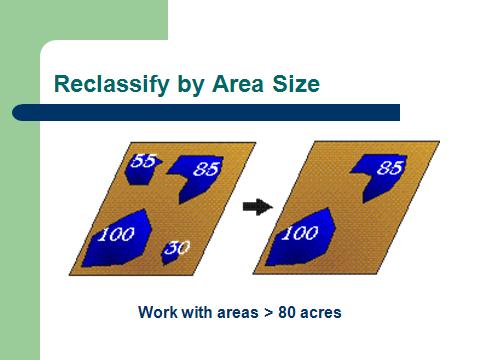
| GIS Analysis Functions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
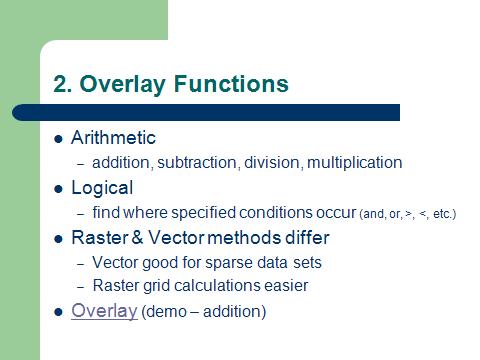
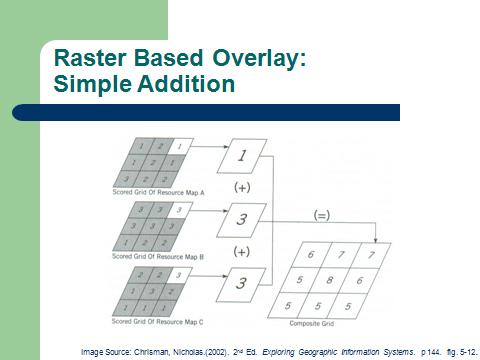
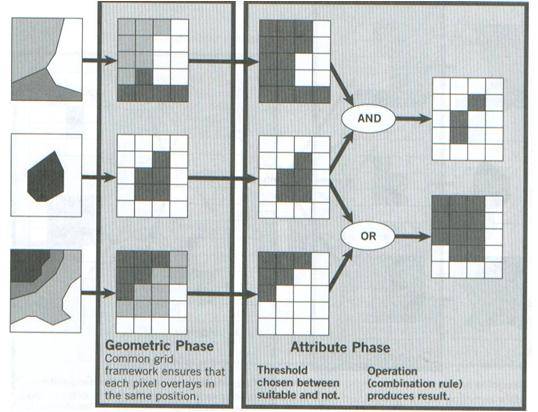
Raster overlay boolean composition |
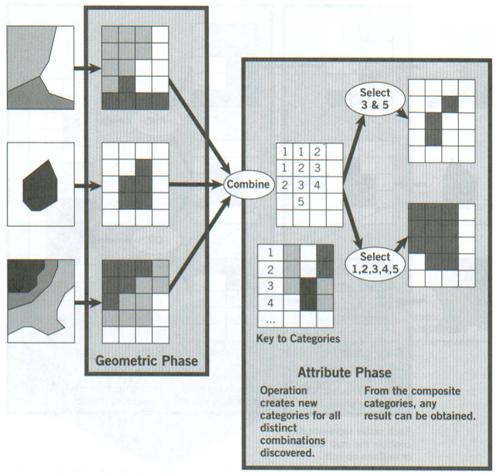
Raster overlay composite combination |
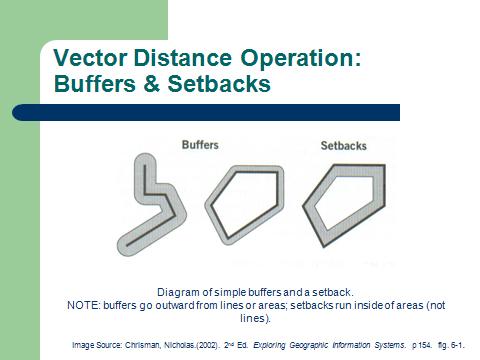
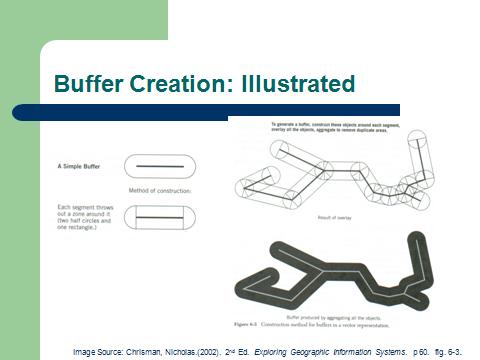
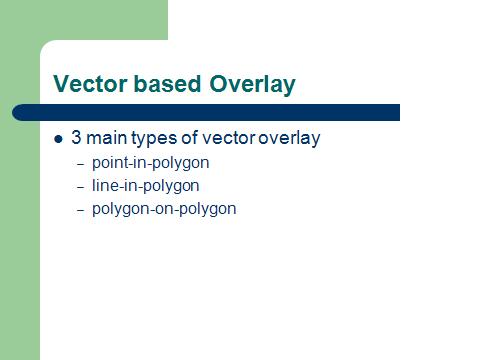
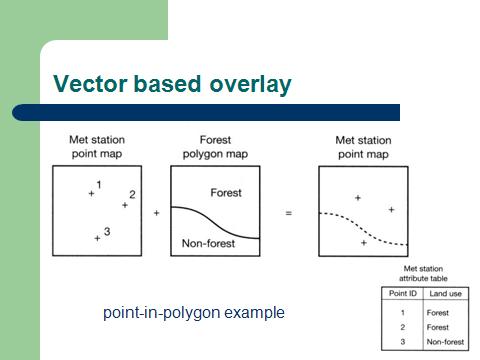
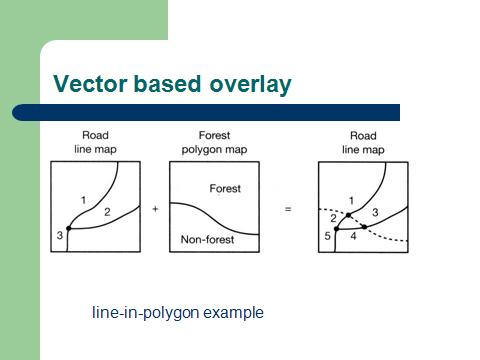
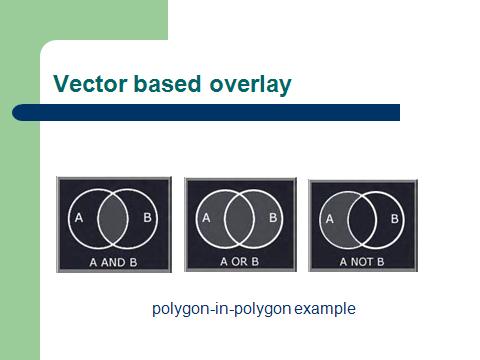
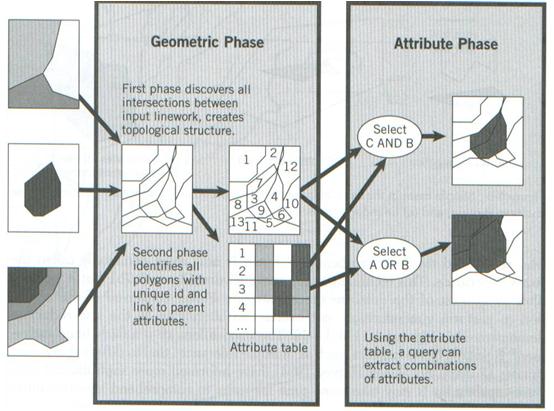
Vector composite structure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Entity ¢ an individual point, line or area in a GIS Database
Attribute ¢ data about an entity stored in a database (the street name for a line; in raster GIS ¢ code for cell; for example ō1ö can be for a motorway, ō2ö for main roadģ linked to the raster imige
Feature ¢ an object in the real world to be encoded in a GIS database
Data layer ¢ a data set for the area of interest in a GIS
Image ¢ a data layer in a raster GIS
Cell ¢ an individual paxel
Function or operation ¢ a data analysis procedure performed by a GIS
Algorithms ¢ the computer implementation of a sequence of actions designed to solve a problem
GIS Data
n What types of data does a GIS need to
represent?
n Continuous
Ģ Data takes on a wide range of values
Ģ Data values do not represent themes or classes,
but rather a specific variable
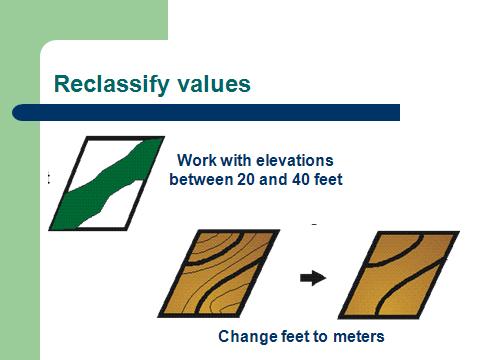
¢ E.g. Elevation= 4.534 m
n Discrete/Thematic/Categorical
Ģ Feature represents a discrete class
¢ E.g. Interstate highway, Forest, Tree stem
Ģ Data stored is a code that represents a class
¢ E.g. 1= oak, 2=maple, 3=hickory
Images
Ģ Form of continuous data where the
variable being represented is brightness
Ģ Can include multiple ōbandsö representing
brightness in different spectral ranges
Raster
Ģ Break the area being represented into
ōpixelsö (picture elements)
Ģ Assign each pixel a value that may
represent continuous or discrete values
Vector Representations
n Use points and lines to represent
features. Polygons are represented by
boundaries
Tools for Raster/Grid Data
n Spatial Analyst provides raster
processing capabilities in ARCGIS
n The Raster Calculator is a powerful tool
for combining data layers to produce
new raster data layers
Raster GIS Measurements: Pythagorean distance; Manhattan distance; proximity distance; perimeter and area
The Power of Raster
Analysis of raster data is particularly useful
for:
n Determining least-cost paths for traversing
a landscape without roads
n Modeling habitat requirements for species
n Working with elevation or bathymetric data
n Summarizing characteristics of areas
n Analyses where variations in proximity are
important
What are the areas of an island that can
be colonized by shrubs?
n What level of land elevation must be
achieved before shrubs colonize?