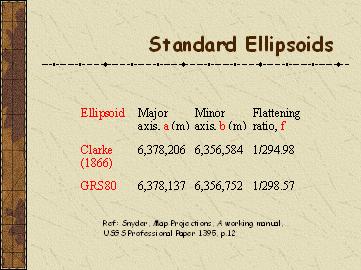
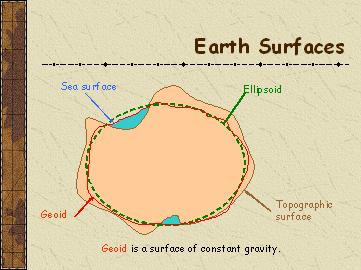
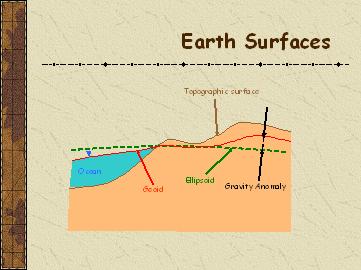
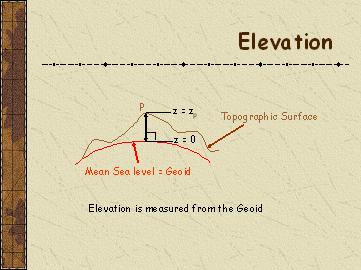
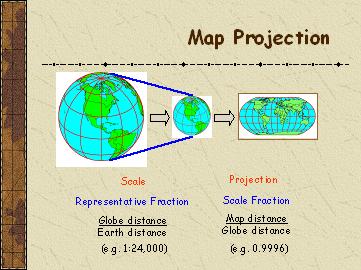
| Map Projection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The equirectangular projection with Tissot''s Indicatrix of deformation |
Kinds of Map Projections
We have two kinds of Map Projections
according to their usage:
��Geodetic Projections
��Cartographic Projections
Projections for mapping of countries, nations or great
landmasses assuming the shape of the earth as ellipsoid.
Projections for mapping the whole world assuming the
shape of the earth as sphere.
Types of Map Projections
We have two types of Map Projections
according to their generation:
��True Projections
��Pseudo Projections
The transformation from datum to projection surface is
geometrical or semi-geometrical.
The transformation from datum to projection surface is
only mathematical.
Classification of Map Projections
��Nature of the projection surface defined as geometric
figure
��(aCzimouitnhacl, icdyleinndecre, coonri cc aonnd tmaicscte lolafn etohues )projection surface with the
datum surface (tangent or secant �)
��Position or alignment of the projection surface with
relation to the datum surface (polar, equator, oblique
Class I
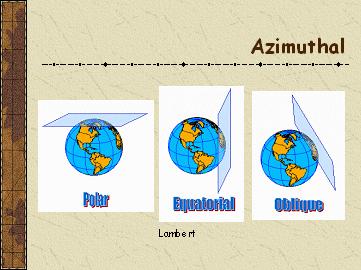
��Azimuthal Projections
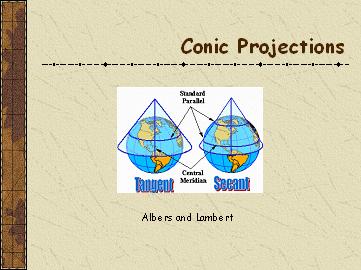
��Conical Projections
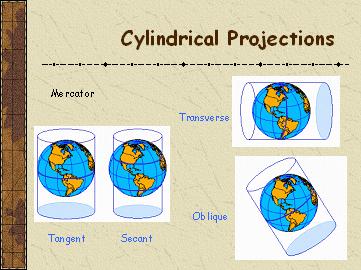
��Cylindrical Projections
Class II
��Tangent Projections
��Secant Projections
��Polysuperficial projections
Class III (The aspects of map projections)
��Normal Projections
��Transverse Projections
��Oblique Projections
Properties of Map Projections
��Equidistance : correct
representation of distances
��Conformality: correct
representation of shapes
��Equivalency : correct
representation of areas
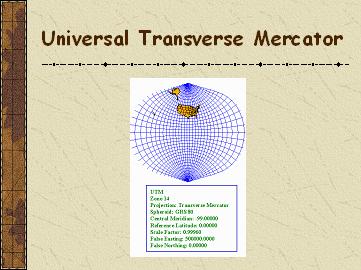
UNIVERSAL TRANSVERSE MERCATOR
PROJECTION (UTM)
� cylindrical, equatorial, conform projection
� the area is covered by 80� South - 84� North latitude
� the earth is divided into 60 zones (each 6� longitude)
� 180� West Longitude - 0� - 180� East Longitude
� 20 latitudinal belts (each 8� latitude)
� scale factor = 0.9996
� origin shifted 500 000 m to east (false easting)
� origin shifted 10 000 000 m to south for the southern
hemisphere
� the Hayford ellipsoid, the ED50 datum
The theory of distortions
If a rectangular system of parametric curves has been
selected on the datum surface, the corresponding set of
curves on the projection plane is as a rule nonrectangular.
Tissot has proven that �in every point of the datum
surface a set of rectangular parametric curves exists
which has a corresponding set of the same
characteristics in the projection plane�.
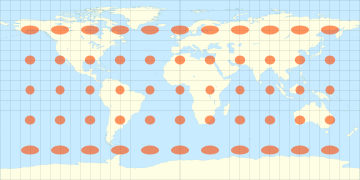
These are called the principal parametric curves - Deformations on Map Projections
Tissot�s indicatrix
The parameters of the deformation ellipse
The Choice of the suitable map projection
on example of secant conic projections
Classification and properties
Azimuthal Equidistant
Classification: Azimuthal, Neither conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Polar, oblique and equatorial
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Center
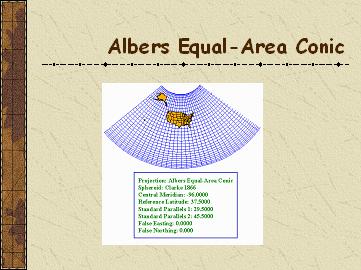
Albers EqualArea Conic
Classification: Conic, Equal area
Aspects: Polar, oblique
Earth Shape: Sphere, Ellipsoid
True Scale at: Parallel through center , between standard parallels
Bonne
Classification: Pseudo-Conic, Equal area
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere, Ellipsoid
True Scale at: Central meridian, all parallels
Cassini
Classification: Cylindrical, Neither conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Transverse
Earth Shape: Sphere, Ellipsoid
True Scale at: Central meridian and lines perpendicular to it
Central Clindrical
Classification: Cylindrical, Perspective neither conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Equatorial
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Equator
Dutch RD
Classification: Stereographic Double projection, conformal
Aspects: Oblique
Earth Shape: Ellipsoid
True Scale at: Ellips around Center
Eckert I
Classification: PseudoCylindrical, Neither conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere
Eckert II
Classification: PseudoCylindrical, Equal area
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere
Eckert III
Classification: PseudoCylindrical, Neither conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere
Equidistant Conic
Classification: Conic, Neither Conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere, Ellipsoid
True Scale at: All meridians and central parallel
General Perspective
Classification: Azimuthal, Neither conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Polar, oblique, equatorial
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Center
Gnomonic
Classification: Azimuthal, Neither conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Polar, oblique and equatorial
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Center
Hammer Aitoff
Classification: Modified Azimuthal, Equal area
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere, Ellipsoid
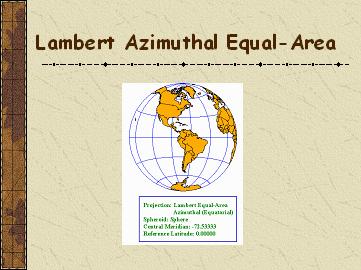
Lambert Azim EqualArea
Classification: Azimuthal, Equal area
Aspects: Polar, oblique and equatorial
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Center
Lambert Conform Conic
Classification: Conic, Conformal
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere, Ellipsoid
True Scale at: Central parallel
Mercator
Classification: Cylindrical, Conformal
Aspects: Equatorial
Earth Shape: Sphere, Ellipsoid
True Scale at: Equator
Miller
Classification: Cylindrical, Neither conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Equator
Mollweide
Classification: PseudoCylindrical, Equal area
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Parallels 40grd44'' N and S
Oblique Mercator
Classification: Cylindrical, Conformal
Aspects: Oblique
Earth Shape: Sphere, Ellipsoid
True Scale at: Central Curve
Orthographic
Classification: Azimuthal, Neither conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Polar, oblique and equatorial
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Center
Plate Carree
Classification: Cylindrical, Perspective, neither conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Equatorial
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Equator and all meridians
Plate Rectangle
Classification: Cylindrical, Perspective, neither conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Equatorial
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Two parallels equidistant from equator, all meridians
PolyConic
Classification: PolyConic, Neither conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere, Ellipsoid
True Scale at: Central meridian, each parallel
Robinson
Classification: PseudoCylindrical, Conformal
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Equator
Sinusoidal
Classification: PseudoCylindrical, Equal Area
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Equator
Sinusoidal Interrupted
Classification: PseudoCylindrical, EqualArea
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Equator
Sinusoidal 3x Interrupt
Classification: PseudoCylindrical, EqualArea
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Equator
StereoGraphic
Classification: Azimuthal, Conformal
Aspects: Polar, oblique and equatorial
Earth Shape: Sphere, Ellipsoid
True Scale at: Center
Transverse Mercator, Gauss-Kruger
Classification: Cylindrical, Conformal
Aspects: Transverse
Earth Shape: Sphere, Ellipsoid
True Scale at: Central meridian
UPS
Classification: Azimuthal, Conformal , special stereographic
Aspects: Polar
Earth Shape: Ellipsoid
True scale at: Circle around pole
UTM
Classification: Cylindrical, Conformal, special transvers mercator
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Ellipsoid
True Scale at: Two straight lines (not meridians!) eqidistant to Central Meridian
VanderGrinten
Classification: Miscellaneous, Neither conformal nor equal area
Aspects: Normal
Earth Shape: Sphere
True Scale at: Equator